[ad_1]
It began off as an enigma. Biologists at house internet sites world huge reported that frogs had merely disappeared. Costa Rica, 1987: the golden toad, lacking. Australia, 1979: the gastric brooding frog, gone. In Ecuador, Arthur’s stubfoot toad was final seen in 1988.
By 1990, instances of unexplained frog declines have been piling up. These weren’t remoted incidents; it was a worldwide sample – one which we now know was as a consequence of chytridiomycosis, a fungal illness that was infecting and killing an infinite fluctuate of frogs, toads and salamanders.
Our analysis, printed in the intervening time in Science, reveals the worldwide variety of amphibian species affected. No less than 501 species have declined as a consequence of chytrid, and 90 of them are confirmed or believed extinct.
Research further:
The place did the frog pandemic come from?
When biologists first started to evaluation the mysterious species disappearances, they have been at a loss to elucidate them. In a variety of instances, species declined shortly in seemingly pristine habitat.
Species declines usually have apparent causes, akin to habitat loss or launched species like rats. Nonetheless this was totally completely completely different.
The primary huge breakthrough acquired proper right here in 1998, when a bunch of Australian and worldwide scientists led by Lee Berger found amphibian chytrid fungus. Their analysis confirmed that this uncommon fungal pathogen was the reason for frog declines all through the rainforests of Australia and Central America.
Nonetheless, there have been nonetheless many unknowns. The place did this pathogen come from? How does it kill frogs? And why have been so many alternative species affected?
After years of painstaking analysis, biologists have stuffed in a variety of devices of the puzzle. In 2009, researchers found how chytrid fungus kills frogs. In 2018, the Korean peninsula was pinpointed on account of the most likely origin of primarily most likely essentially the most lethal lineage of chytrid fungus, and human dispersal of amphibians instant as a possible present of the worldwide unfold of the pathogen.
Nevertheless on account of the thriller was slowly however truly unravelled, a key query remained: what number of amphibian species have been affected by chytrid fungus?
Early estimates instant that about 200 species have been affected. Our new evaluation reveals the full is sadly masses bigger: 501 species have declined, and 90 confirmed or suspected to have been killed off altogether.
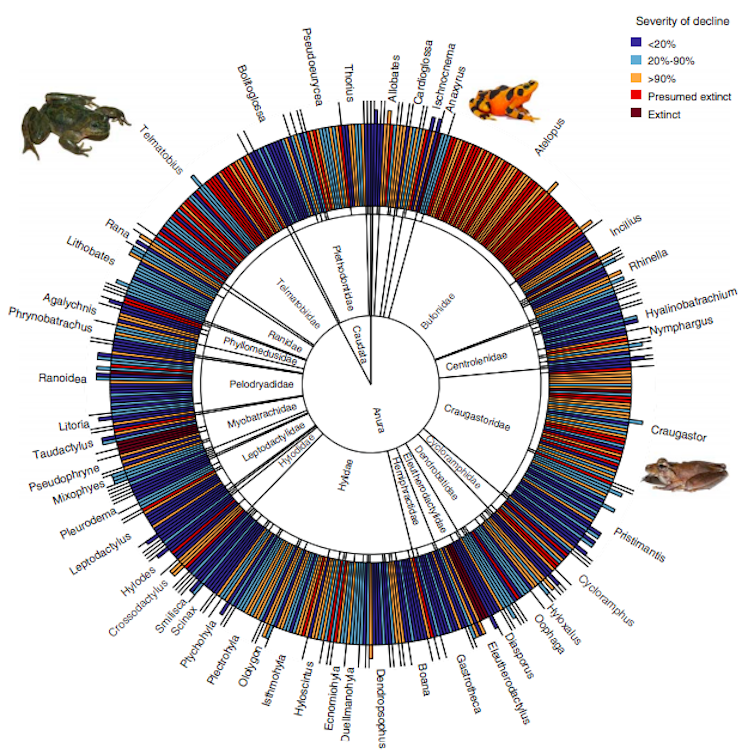
Scheele et al. Science 2019
Devastating killer
These numbers put chytrid fungus all through the worst league of invasive species worldwide, threatening comparable numbers of species as rats and cats. The worst-hit areas have been in Australia and Central and South America, which have many alternative frog species, together with superb circumstances for the expansion of chytrid fungus.
Giant species and different individuals with small distributions and elevational ranges have been the largely liable to expertise extreme declines or extinctions.
Along with 41 amphibian consultants from world huge, we pieced collectively data on the timing of species declines utilizing printed knowledge, survey knowledge, and museum collections. We discovered that declines peaked globally all through the Nineteen Eighties, about 15 years earlier than the illness was even found. This peak coincides with biologists’ anecdotal analysis of bizarre amphibian declines that occurred with rising frequency all through the late Nineteen Eighties.
Encouragingly, some species have confirmed indicators of pure restoration. Twelve per cent of the 501 species have begun to recuperate in some areas. Nonetheless for the overwhelming majority of species, inhabitants numbers are nonetheless far beneath what they as shortly as have been.
Many of the troubled species haven’t nonetheless begun to bounce as soon as extra, and plenty of proceed to say no. Speedy and substantial motion from governments and conservation organisations is required if we’re to maintain up these species off the extinct pointers.
Research further:
Saving amphibians from a lethal fungus means performing with out figuring out all of the choices
In Australia, chytrid fungus has induced the decline of 43 frog species. Of those, seven in the intervening time are extinct and 6 are at excessive threat of extinction as a consequence of most and ongoing declines. The conservation of those species relies upon upon focused administration, such on account of the restoration program for the enduring corroboree frogs.
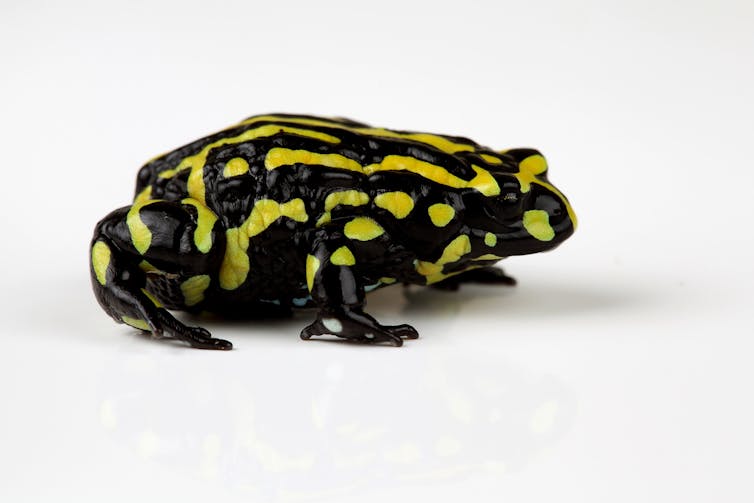 The southern corroboree frog: hopefully not a disappearing icon.
The southern corroboree frog: hopefully not a disappearing icon.Importantly, there are nonetheless some areas of the world that chytrid has not nonetheless reached, akin to New Guinea. Stopping chytrid fungus spreading to those areas would require a dramatic low value all through the world commerce of amphibians, together with elevated biosecurity measures.
The unprecedented deadliness of a single illness affecting an entire class of animals highlights the necessity for governments and worldwide organisations to take the specter of wildlife illness severely. Dropping further glorious species an identical to the golden toad and gastric brooding frog is a tragedy that we’re able to keep away from.
[ad_2]
